If you’re preparing for the United States Medical Licensing Examination® (USMLE®) Step 2 exam, you might want to know which questions are most often missed by those taking the practice test. Check out this example from Kaplan Medical, and view an expert video explanation of the answer. Also check out all posts in this series.
A 43-year-old woman with HIV comes to the physician because of painful swallowing, substernal chest pain and weight loss for one month. She takes no medications. Her temperature is 37.8 °C (100 °F). Her CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 41/mm3. Upper endoscopy shows inflammation and a large, deep ulceration of the distal esophagus. A biopsy specimen of the esophagus shows inflammation and small blood vessel endothelial cells with markedly enlarged, smudgy, eosinophilic nuclei. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
A. Acid reflux
B. Candida
C. Cytomegalovirus
D. Herpes simplex
E. Herpes zoster
The correct answer is C.
Kaplan Medical explains why
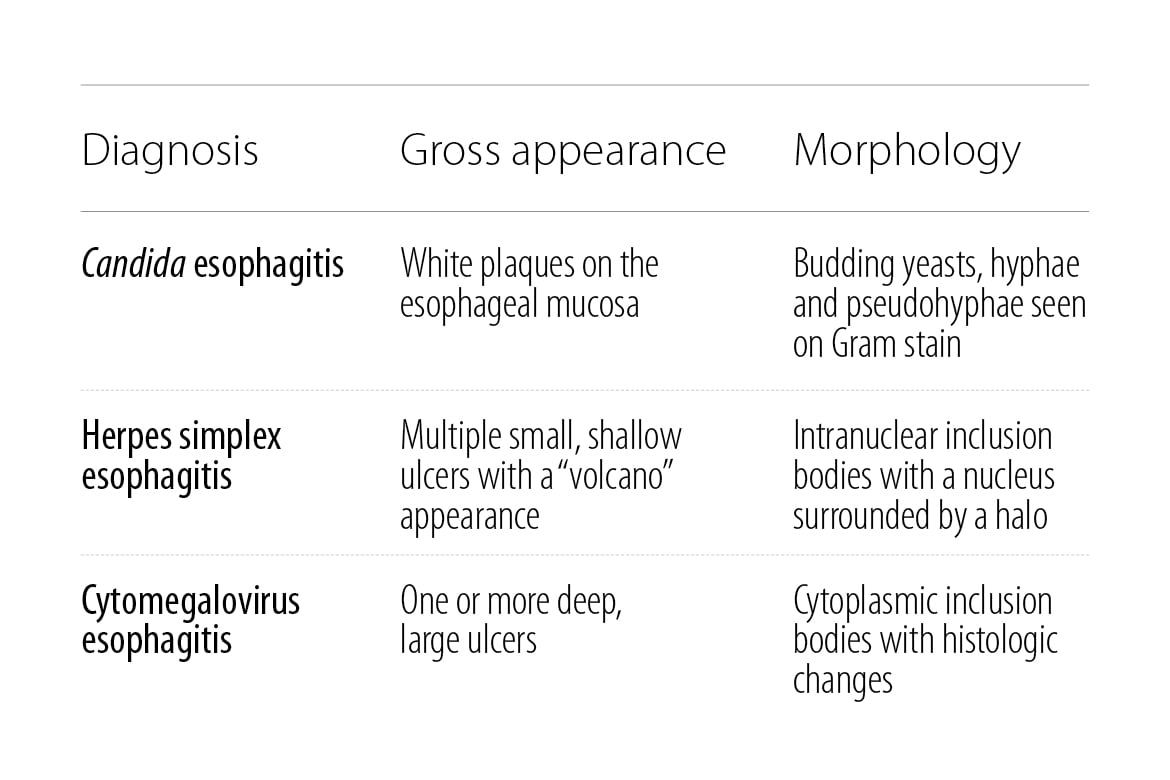
Patients who have AIDS and other profoundly immunosuppressed patients are vulnerable to infectious esophagitis. Endoscopy with biopsy is used to identify the causative agents, which are typically Candida, herpes simplex or cytomegalovirus. If an AIDS patient presents with odynophagia, treatment should initially be empiric against Candida. If empiric treatment fails, endoscopy is warranted to differentiate between herpes simplex and cytomegalovirus infection. Careful review of the biopsy specimen material is necessary, because these patients may actually be infected by more than one organism. In the case of cytomegalovirus infection, the distinctive histologic finding is the presence of small numbers of cells with markedly enlarged nuclei, which will show intranuclear viral inclusions. Manifestations of cytomegalovirus in HIV/AIDS patients are more common when patients have a CD4+ T-cell count less than 50/mm3. Cytomegalovirus infection can be treated with ganciclovir.
Why the other answers are wrong
Read these explanations to understand the important rationale for why each answer is incorrect.
Choice A: Acid reflux could produce inflammation, but it would be unlikely to show ulceration of the esophagus.